The Significance of Patient Preparedness in Focused Common Bile Duct Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Choledocholithiasis
Abstract
Choledocholithiasis, the presence of gallstones
in the common bile duct, poses a diagnostic challenge due to its varied
presentation. Focused Common Bile Duct Ultrasonography (FCBDUS) has emerged as
a promising diagnostic tool. However, the significance of patient preparedness
in FCBDUS remains underexplored
Objective: This research aims to elucidate
the impact of patient preparedness (2-4 hours Fasting and Drinking atleast 2
glass of water before ultrasonography) on the accuracy and efficacy of FCBDUS
in diagnosing choledocholithiasis.
Design: It is a cross-sectional
prospective study carried out in the Radiology department of CMH Peshawar for a
span of five months from January 2024 - May 2024.
Setting: Radiology department of CMH
Peshawar. STUDY DURATION: 1st January 2024- 15th May 2024.
Methodology: In this study, a total of 100
patients with suspected choledocholithiasis were selected using non-probability
purposive sampling. Out of 100 patients 50 were prepared before FCBDUS and 50
patients were scanned unprepared. Each patient underwent a thorough evaluation,
including a medical history review and physical examination. Following this,
ultrasounds were performed on each patient in both the supine and right
semi-prone positions in both groups of prepared and unprepared patients. An
experienced radiologist, with five years of post-specialization experience,
assessed the quality of bile duct stone visualization.
Results: The visualization quality of bile
duct stones was significantly higher in the right semi-prone position with
well-prepared patients as compared to the supine position and unprepared
patients before focussed CBD ultrasound. Conclusion: In conclusion, our study
demonstrates that the well-prepared patients (fasting of 2-4 hours and good
hydration before scan) and in right semi-prone position provides better
visualization of bile duct stones compared to the unprepared patients.
Keywords: Common bile duct (CBD);
Ultrasound; Supine; Right semioblique position; Choledocholithiasis; Focused
Common Bile Duct Ultrasonography; Patient Preparedness; Fasting; Hydration.
Introduction
Choledocholithiasis,
characterized by the presence of gallstones within the common bile duct, can
lead to serious complications such as cholangitis and pancreatitis1. Timely and
accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management2. While various imaging
modalities exist, FCBDUS has gained attention for its non-invasiveness,
cost-effectiveness and portability3. However, the role of patient preparedness,
including fasting status and hydration, remains poorly understood4,5.
Methodology
A
prospective analysis was conducted on patients who underwent FCBDUS for
suspected choledocholithiasis over a period of five months. Data including
patient demographics, fasting duration and hydration status were collected.
Statistical analysis was performed to assess the association between patient
preparedness factors and FCBDUS accuracy. Patient preparedness include the
following:
• Fasting
Requirements: One of the primary preparations for CBD ultrasonography is
fasting. Fasting for at least 2-4 hours at least before the examination ensures
that the gallbladder is distended and reduces the presence of bowel gas, which
can obscure the visualization of the bile ducts. Studies have shown that
fasting improves the clarity of ultrasound images, thereby enhancing the
detection of bile duct stones.
•
Hydration Status: Adequate hydration is essential as it helps maintain the
echogenicity of the bile duct and surrounding structures, making it easier to
identify abnormalities.
Results
Preliminary
findings indicate a significant correlation between fasting duration and FCBDUS
efficacy. Patients who adhered to recommended fasting guidelines exhibited
clearer imaging and higher diagnostic accuracy compared to noncompliant
individuals. Hydration status also showed a notable impact, with adequately
hydrated patients demonstrating improved visualization of the common bile duct.
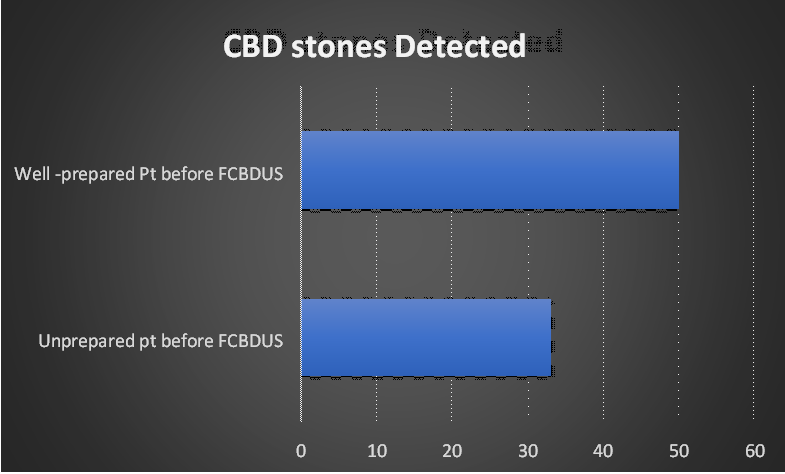
Visualization
of CBD stones in group A (well prepared before FCBDUS) was cent percent in
making exact diagnosis as compared to the non-prepared patient (Group-B). As
shown below in (Table 1), (Figure 1).
Table 1: Patient preparedness include the fasting of at least 2-4 hours before the scan and good hydration before the FCBDUS
|
Patient |
Total No. of patients |
FCBDUS CBD stone |
FCBDUS- No CBD stone detected |
Accuracy |
|
|
Preparedness |
detected |
||||
|
Well -prepared before FCBDUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
50 |
50 |
0 |
100% |
||
|
Not prepared before FCBDUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
50 |
33 |
17 |
66% |
||
|
|
|||||
The percentage accuracy can be shown in (Figure
2) below
Figure 2: The Percentage
Accuracy of CBD stone Detection
Discussion
The findings
underscore the importance of patient preparedness in optimizing FCBDUS for
diagnosing choledocholithiasis6.
Adequate fasting duration and hydration positively influence image quality,
thereby enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of FCBDUS7. These results highlight the need for
standardized protocols regarding patient preparation to maximize the utility of
FCBDUS in clinical practice8.
Proper patient preparedness directly impacts the diagnostic accuracy of CBD
ultrasonography9. Inadequate preparation
can lead to poor image quality, resulting in missed or false diagnoses of
choledocholithiasis10. Ensuring
patients are well-prepared can reduce the need for repeat examinations, thereby
saving costs and reducing patient exposure to additional procedures and
potential delays in diagnosis11,12.
Several studies
have highlighted the importance of patient preparation in the success of CBD
ultrasonography13,14,15. For
instance, a study by Sarwar et al. (2020) demonstrated that patients who
adhered to fasting guidelines had significantly higher rates of accurate
diagnosis compared to those who did not16.
Another study by Gupta et al. (2019) emphasized the role of patient education
in reducing anxiety and improving cooperation during the procedure, thereby
enhancing image quality and diagnostic yield17.
Conclusion
Patient preparedness significantly influences the diagnostic accuracy of
FCBDUS for choledocholithiasis. Establishing guidelines for fasting duration
and hydration status can improve imaging quality and enhance the efficacy of
FCBDUS as a diagnostic tool. Further prospective studies are warranted to
validate these findings and establish standardized protocols for patient
preparation in FCBDUS. Patient preparedness plays a critical role in the
effectiveness of focused common bile duct ultrasonography for diagnosing
choledocholithiasis. Proper fasting, hydration, positioning and psychological
readiness contribute to optimal imaging conditions, enhancing the accuracy and
reliability of the diagnosis. Continued emphasis on patient education and
preparation protocols is essential to improve clinical outcomes and reduce
healthcare costs associated with repeat imaging and misdiagnosis.
References
15. Tammaro S, Caruso R, Pallone F, Monteleone G. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography pancreatitis: Is time for a new preventive approach? World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:4635-4638.
16. Sarwar A, et al. Impact of Fasting on Ultrasound Imaging of the Biliary System. J Medical Imaging 2020.
17. Gupta R, et al. Patient Anxiety and Cooperation in Ultrasound Procedures. J Patient Experience 2019.