The Efficiency of Distributed Cloud Computing in AI Models
Citation: Srinivasa Kalyan Vangibhurathachhi. The Efficiency of Distributed Cloud Computing in AI Models. J Artif Intell Mach Learn & Data Sci, 2025, 3(1): 1-7.
Copyright: ©2025 Srinivasa Kalyan Vangibhurathachhi. This is an
open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any
medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
The rapid advancements in Artificial
Intelligence (AI) have led to increased computational demands, particularly for
deep neural networks (DNNs) and large language models (LLMs). Traditional
centralized cloud computing struggles to efficiently support AI workloads due
to high latency, bandwidth constraints, energy inefficiencies and scalability
limitations. To address these challenges, Distributed Cloud Computing (DCC) has
emerged as an innovative platform that decentralizes computational resources,
bringing them closer to data sources to enhance efficiency, reduce costs and
optimize performance. This paper critically examines the efficiency of DCC in
AI models.
Through
decentralized resource allocation, optimized workload distribution and
real-time data processing, DCC offers benefits such as lower latency, improved
computational scalability, energy efficiency, resource utilisation, data
privacy and compliance. A comparative analysis with centralized and edge cloud
models highlights the advantages of DCC, particularly in latency reduction,
high scalability, throughput and energy efficiency. Additionally, key use cases
in autonomous vehicles, healthcare, finance and retail highlight DCC’s
transformative potential across industries. Further, future trends in DCC for
AI models are focussed on; quantum cloud computing for AI model acceleration,
integration of 5G in distributed cloud systems and AI-drive distribute cloud
orchestration. Despite its benefits, security vulnerabilities, workload
management complexities and significant computational resources which are
needed remain key challenges. Addressing these issues will be crucial for
maximizing AI efficiency in the era of distributed computing.
Keywords: Distributed cloud computing (DCC), edge computing, federated
learning, centralised cloud infrastructure, AI model, efficiency.
1.
Introduction
Artificial intelligence is transforming industries
from finance and healthcare to entertainment, autonomous systems and smart
cities. However, the current AI models such as deep neural networks (DNNs) and
large language models (LLMs) demand massive computational resources for
training and real-time inference1. To
address the growing computational demands of AI applications, the integration
of AI with cloud computing has emerged as a promising approach2. By leveraging the scalability, cost-effectiveness,
flexibility and collaborative opportunities provided by cloud computing,
practitioners and researchers can develop and deploy innovative AI solutions
across a wide range of domains for various industries.
However, Abughazalah, et al.3 noted that the traditional centralized cloud infrastructures present challenges such as latency, cost, bandwidth limitations and energy inefficiencies especially when handling massive datasets required for training complex AI models. In addressing these issues, distributed cloud computing (DCC) has emerged as a promising paradigm that decentralises data processing by bringing computational resources closer to data sources4. Unlike traditional cloud models that centralizes resources, DCC focuses on dispersing resources to specific data centre locations to enhance performance and scalability while reducing latency, bandwidth constraints and operational costs4. Leading companies such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure have developed and adopted distributed architectures to enhance AI model efficiency and scalability2.
To this end, this research paper explores the
efficiency of distributed cloud computing in AI models by;
- Evaluating the
efficiency of DCC in AI workloads
- Comparing DCC
performance with
centralized and hybrid computing architectures.
- Analysing its impact on cost,
latency, energy consumption and scalability
- Identifying key challenges and proposing future directions for distributed cloud computing in AI models.
2. Problem Statement
In the views of Zangana, et al5, the traditional AI computing models rely on centralized cloud data centres which
face significant bottlenecks when processing large scale AI workloads. For
instance, the need to transfer vast amounts of data to centralized data centres
results in high latency and bandwidth consumption, thus affecting the
performance of AI applications particularly for those requiring real-time
processing like internet of things and autonomous vehicles. Abughazalah, et al.3 adds that centralized AI systems require large-scale data centres which involve
high capital and operational expenses.
In case of technical problems, centralized systems can become single points of
failure thus raising concerns about reliability and resilience. Moreover, the
energy demands of large data centres substantially to the operational costs and
carbon footprints of centralised data centres6.
While traditional AI computing present significant
bottlenecks, challenges also exist in AI model training and deployment. Nama7 argues that training AI models requires
considerable computational power and storage capacities. Accordingly,
centralized cloud systems may struggle to efficiently allocate resources for
parallel processing tasks, leading to suboptimal performance. Additionally, the
data privacy and security are critical concerns when transferring sensitive
information to centralized locations due to the increased risk of breaches.
Medium8 reports that ensuring
compliance with data protection regulations in various countries and regions
further complicates the training and deployment of centralized AI models. To
overcome these limitations, DCC
which enables AI workloads to be executed across multiple cloud environments, hybrid clouds and edge nodes is crucial9. This improves performance, cost-effectiveness and sustainability while reducing
dependency on single-location processing.
Figure
1: Challenges in AI model training (Tikong, 2024).
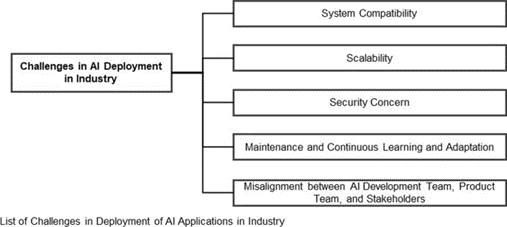
Figure 2: Challenges in AI model deployment (Sinha & Lee, 2024).
3. Proposed Solution: Distributed Cloud Computing for
AI Models Efficiency
3.1. What is DCC
By definition, DCC refers to the decentralized allocation of computational
resources across multiple data centres including public, private, hybrid and edge clouds10.
With this targeted and centrally managed distribution of public cloud services,
businesses can deploy and run applications in a mix of cloud environments that
meet their requirements for performance, regulatory compliance and much more.
Ramamoorthi11 highlights that DCC
resolves the operational and management inconsistencies which occur in
centralised cloud or multicolour environments. Most importantly, DCC offers the
ideal foundation for edge computing which involves running servers and
applications closer to where data is created12.
Key technologies have enabled DCC include; containerization and orchestration13
and serverless AI computing
technologies14,15. Other technologies
that are useful in DCC are; Federated AI and decentralized learning (TensorFlow Federated, PySyft)16 and AI-optimized
hardware accelerators (Tensor Processing Units, Field Programmable Gate
Arrays, Graphics Processing Units clusters)17.
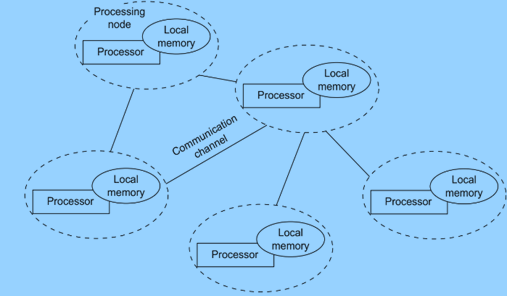
Figure 3: DCC (Abdi
& Zeebaree, 2024).
3.2. How distributed cloud computing enhances AI
efficiency
Extant literatures and empirical studies indicate that
DCC can improve the efficiency of AI models through various ways. Ramamoorthi11 highlight that DCC reduces latency in AI
applications such as those requiring real-time processing like autonomous
vehicles and financial fraud detection. Although traditional cloud-based AI
processing requires sending data to centralized servers which leads to latency
issues, distributing workloads closer to data sources through edge computing
significantly reduces processing times11.
Sengupta18 reports that Google's Edge TPU technology utilizes
distributed cloud frameworks to process AI workloads closer to the source thus
reducing delays in AI applications like speech recognition and real-time video
analytics.
DCC systems can improve the efficiency of AI models
through optimised resource allocation. Although traditional cloud models tend
to suffer from inefficient resource allocation where certain data centres
remain underutilized, distributed systems addresses this issue by allocating
computational tasks across various nodes within the network based on demand19. Such an approach maximizes performance of
individual nodes and enhances the responsiveness and efficiency of systems.
This evident in AWS where Lambda
and Fargate offer serverless computing by allowing AI
workloads to be distributed dynamically without requiring dedicated resources
thus reducing operational costs14.
Abdi and Zeebaree19
adds that DCC can improve AI efficiency through parallel processing where
computational workloads are distributed across multiple nodes. This enhances
the efficiency of model training by leveraging parallelism in computation-heavy
tasks such as deep learning-based image classification or NLP model training.
By leveraging capabilities of several computers, parallel processing effectively
addresses the computational demands of intricate and resource-intensive tasks.
Youvan cited OpenAI’s GPT-4 model training which uses distributed computing
across multiple data centres to optimize parallel processing thus reducing
training time compared to single-node computations.
Differently, Nama7
points out that DCC improves AI efficiency through reduction in energy
consumption. While centralised data centres consumers’ massive amounts of
energy, distributed AI models can leverage edge computing to significantly
reduce power consumption. A study by Huang, et al20.
indicated that DCC can reduce power consumption by between 19%-28% through
reducing the need for constant data transfers. Another way in which distributed
systems enhances efficiency of AI models is through scalability which enables
efficient management of increased workload. By augmenting the distributed
systems with additional nodes as needed, Khan21
noted that distributed systems remain capable of handling increasing
computational demands. Vertical scaling (increasing resources of nodes) and
horizontal scaling (adding more nodes) are common approaches to accommodating
increased workload and maintaining operational efficiency22. Scalability is exhibited by Microsoft
Azure’s AutoML platform which uses distributed computing to dynamically scale
AI models training across several cloud regions thus enhancing the processing
power for complex machine learning tasks23.
However, poorly controlled scaling may reduce overall performance of AI models22.
More important, distributed systems can enhance AI
model efficiency and performance through data privacy and compliance by
processing extensive data within a specific region rather than transferring
them to centralised cloud servers2.
Given that data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA impose strict
controls on data processing and storage, distributed cloud servers help in
this. Through federated learning, a distributed AI approach, Thakur24 noted that AI models are trained across
multiple and decentralized devices while keeping data local, enhancing privacy
and reducing computational burden on servers. While distributed systems can
enhance data privacy, Chavan and Raut25
argued that it introduces vulnerabilities such as data fragmentation and
multi-point attack risks. Ensuring secure communication between distributed
nodes remains a key challenge for tech companies.
4. Used Cases of DCC In AI Applications
Several case studies that demonstrate how DCC is used
in AI models to unlock new capabilities and enhance efficiency for businesses
and industries. A notable example is Netflix which uses distributed cloud-based
AI to provide personalised content recommendations for millions of users around
the world 21. By leveraging
scalability of cloud computing, Netflix analyses large amounts of user data in real-time
to fine tune recommendation algorithms thus delivering highly personalized
experience to users. Another successful case of DCC in AI applications is in
the development of autonomous vehicle where automakers like Tesla utilise
cloud-based AI to analyse data from self-driving cars, train AI models and
improve the performance of autonomous systems21.
These cases demonstrate that DCC offers suitable infrastructure for processing
large datasets as AI drives automation and intelligent decision-making.
Additionally, integration of DCC in AI models is reshaping industries by developing innovative services, improving decision making and enhancing new efficiencies21. In healthcare sector, AI-based cloud platforms have revolutionised patient care and diagnostics. For example, IBM Watson Health deploys AI in distributed IBM Bluemix Clouds for analysing medical records and suggesting treatment options whereas cloud-based AI applications are utilised to predict disease outbreaks and improve hospital resource management26.
In the finance industry, distributed clouds and AI
applications are enhancing customer service, fraud detection and risk
management. JP Morgan exemplifies this by utilising AI-powered cloud platforms
to determine fraudulent transactions in real-time and robot advisors to suggest
personalised financial advice27. In
the retail sector, DCC and AI models are revolutionising innovations like
personalised marketing, dynamic pricing and optimisation of inventories. Amazon
has deployed cloud-based AI applications to process consumer preferences,
forecast supply chain demands and suggest personalized product recommendations
effectively28.
5. Impact Analysis: Efficiency Metrics and Comparative
Evaluations
5.1. Performance metrics for evaluating DCC in AI
models
The effectiveness of DCC in AI models can be evaluated
based on;
- Latency reduction: Distributed
systems significantly reduce latency by distributing computational tasks
closer to data sources. Can be measured through response time (time taken
for an AI model to process input and return an output) and inference time
(how quickly AI model can process and predict outcomes in real-time
application) (Naveen et al., 2021).
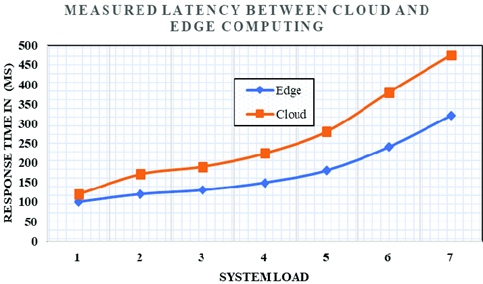
Figure 4: reduced latency due to edge computing29.
- Computational
throughput: Measures how many AI tasks can be processed
simultaneously, directly impacting scalability. AI training models require
massive parallel computations which are measured in petaFLOPS (Floating
Point Operations per Second. Distributed systems allow AI models to run
simultaneously across several nodes, thus increasing throughput30.
- Energy consumption: DCC lowers power
requirements compared to centralized cloud computing and can be measured
in Power Usage Effectiveness (Measures how efficiently data centre uses
energy)31.
- Cost-effectiveness: DCC reduces operational expenses through serverless and dynamic resource allocation. Cost effectiveness can be measured in pay-per-use model where users only pay for the actual compute time consumed by code. This means no more paying for idle servers or underutilized resources32.
5.2. Comparative analysis
A summarised evaluation of DCC AI versus centralised
cloud computing AI and hybrid computing cloud AI is presented as follows;
Table 1: Adapted19,21,11,2.
|
Metric |
Centralized Cloud AI |
Distributed Cloud AI |
Hybrid computing AI |
|
Latency |
High |
Low |
Lowest |
|
Scalability |
Limited |
High |
Moderate |
|
Training Cost |
High |
Moderate |
High (hardware costs) |
|
Data Privacy and security |
Low |
High (federated learning) |
High |
|
Throughput (FLOPS) |
1-10 PFLOPS |
10-100 PFLOPS |
5-50 PFLOPS |
|
Energy Efficiency |
Low |
High |
Moderate |
6.
Scope and Challenges of DCC For AI
6.1.
Future trends and research directions
The
landscape of DCC is continuously evolving with key trends shaping the technological
advancement. A key future trend is the convergence of quantum computing and
distributed cloud which will significantly accelerate AI model training and
inference especially for tasks requiring high-dimensional optimization and
massive parallelism33. This will help
in faster training of deep learning models such as GPT-5 and beyond as well as
optimize neural network weights using quantum-enhanced optimizers. Currently
IBM is testing Quantum Cloud AI for distributed deep learning acceleration to
determine exponential speedups in AI model processing34. Another key trend is the increasing use of
AI to optimise distributed cloud orchestration which enables dynamic resource
allocation, workload balancing and auto-scaling of AI models within distributed
cloud environments. An example is Microsoft’s Azure AI which uses reinforcement
learning to optimize virtual machine allocation thus improving cloud
performance23. Further, Nassef, et
al.35 reported that the emergence of
5G networks will enhance distributed cloud-based AI model performance by
enabling low latency data processing at the edge thereby reducing dependency on
central cloud servers. This will impact real-time AI inference for IoT
applications in smart cities, retail, autonomous vehicles and much more. It
will also lower data transmission costs by processing AI workloads closer to
the source. By understanding these trends in distributed computing organizations
can better harness its potential for scalable and efficient AI model training.
The future research directions should focus on federated learning which has gained significant attention as a method to train AI models across multiple edge devices without sharing raw data, thus addressing privacy concerns24. The research should seek to address challenges in communication overhead within large-scale federated learning networks and ensure model consistency across decentralized training nodes. Verdecchia, et al.36 adds that future researchers should explore the environmental impact of AI model training which has led to the rise of Green AI by focusing on reducing carbon footprints in distributed cloud computing. Key areas of focus should be on energy-efficient AI algorithms that require fewer computations and renewable energy-powered cloud data centres to offset emissions. As AI models are deployed across multi-cloud environments, Jalal et al. observed that future researchers should examine the interoperability issues which arise by requiring standardization in model deployment, deep learning, APIs and data formats. Specifically, researchers should consider Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) which has emerged as a standard framework to ensure AI model portability across different cloud providers.
6.2.
Challenges
Despite
the advantages, AI models in distributed cloud face vulnerabilities such as
data leakage, adversarial attacks and model inversion attacks5. The security may arise from data poisoning
attacks where malicious nodes can inject false data into federated learning
models or adversarial AI hacking where attackers manipulate AI model
predictions through small perturbations. Baranwal, et al37. indicated that privacy and security issues
can be resolved through blockchain-driven AI security which ensures tamper
proof federated learning. Zangana, et al5.
points out complexities in managing distributed AI workload across several
cloud nodes which introduces data synchronization issues, scheduling
inefficiencies and increased orchestration complexity. This challenge can be
resolved by AI-based predictive workload scheduling to optimize cloud resource
allocation. Further, Yuan and Zhou38
pointed that deploying high-performance AI models within distributed cloud
environments requires significant computational resources, which may not be accessible
to all enterprises. Decentralizing AI cloud platforms using blockchain and
shared computational power can help in resolving this issue. Table 2 below
summarizes the key challenges and research opportunities in DCC.
Table
2: DCC challenges11.
7.
Conclusion
Through
decentralized resource allocation, optimized workload distribution and
real-time data processing, DCC offers benefits such as lower latency, improved
computational scalability, energy efficiency, resource utilization, data
privacy and compliance. The study reveals that tech companies like AWS, Google
Cloud and Microsoft Azure have increasingly adopted distributed architectures
to improve AI model performance and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, key use
cases in autonomous vehicles, healthcare, finance and retail highlight DCC’s
transformative potential across industries.
However, several challenges persist, including security vulnerabilities, interoperability issues and workload management complexities. AI models deployed in distributed environments face threats like data leakage, adversarial attacks and compliance risks and significant computational resources which requires solutions. Future research should focus on federated learning advancements, green AI initiatives and quantum-enhanced AI training to further improve DCC and AI model efficiency. As AI continues to evolve, the convergence of DCC with emerging technologies such as 5G, edge computing and quantum computing will shape the future of AI model training and deployment. Overcoming the current challenges will be key in maximizing DCC's potential as the DNA of AI model’s infrastructure thus enabling faster, more secure and scalable AI solutions across various domains.
8. References
4. Samunnisa K, Kumar GSV and Madhavi K. Intrusion detection system in
DCC: Hybrid clustering and classification methods. Measurement: Sensors, 2023;25: 1-12.
6. https://www.restack.io/p/centralized-vs-decentralized-ai-answer-2023-articles
10. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/distributed-cloud
11. Ramamoorthi V. Exploring AI-Driven Cloud-Edge Orchestration for IoT
Applications. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science,
Engineering and Information Technology, 2023;5: 385-393.
14. https://aws.amazon.com/serverless/
17. Hambali Y, Riwurohi JE and Akbar V. Smart Strategies in Hardware
Provisioning for Ai Solutions in The Cloud. Eduvest-Journal of Universal Studies, 2024;4: 11387-11399.
21. Khan F. Artificial Intelligence and Cloud Computing: A Perfect
Symbiosis. Advances in Computer
Sciences, 2023;6: 1-12.
22. Malhotra S. The Current State of Research into the Efficiency of
Distributed Machine Learning Algorithms for Cloud-Based Big Data Analysis. International
Journal of Advance Research, Ideas and Innovations in Technology, 2025;11: 132-134.
23. https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/machine-learning/
34. https://www.forbes.com/sites/tiriasresearch/2024/06/24/ibm-develops-the-ai-quantum-link/
41. Sinha S and Lee YM. Challenges with developing and deploying AI
models and applications in industrial systems. Discov Artif Intelligence, 2024;4.
https://www.eweek.com/artificial-intelligence/how-to-train-an-ai-model/